How to write cron job from linux command

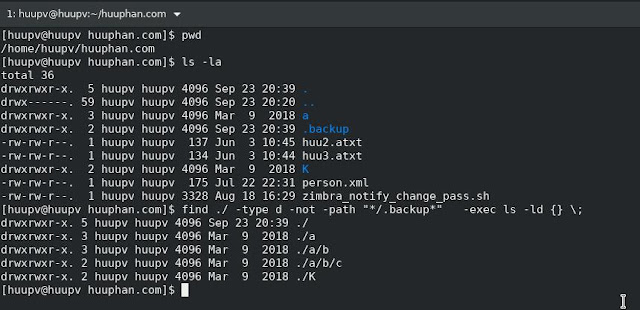
In this tutorial, How do i use linux command write cron job. Crontab example Run cron job At every 15th minute for zimbra_full_backup.sh */15 * * * * /opt/scripts/zimbra_full_backup.sh https://crontab.devopsroles.com/ Write cron job from linux command [root@huupv huuphan.com]# echo "$(crontab -l; echo '*/15 * * * * /opt/scripts/zimbra_full_backup.sh')" | crontab - The screen output terminal: Conclusion Thought the article, How to write cron job from linux command as above . I hope will this your helpful.